Comparison Standards Between LED Light Energy Efficiency Standards in north America, Europe and China
18-11-2015LED light might be a new lighting product, but it is being widely applied in different types of lighting applications, according to a report from Chinese-language Emerging Industry Strategic Library. To improve energy saving technologies, many countries have issued their own LED light standards. Lighting was included in China’s energy efficiency standards, which became effective in January 2008, while the Energy Star in theU.S.has made certain energy efficiency standards during the certification process. The EU directive on energy-related products (ErP) covers LED light energy savings.
1. China’s Energy Efficiency Label
In recent years,Chinahas been investing more money in the research of LED light standards. The country has established energy efficiency and performance standards for non-directional self-ballasted LED lights.
1.1 Non-directional self-ballasted LED lights energy efficiency requirements
According to GB30255-2013 regulations, non-directional self-ballasted LED lights can be classified into omnidirectional, half-omnidirectional (180 degree beam angle) and semi omnidirectional lights. There are three energy efficiency classes based on the starting lighting efficacy (lm/w), as seen in the table below.
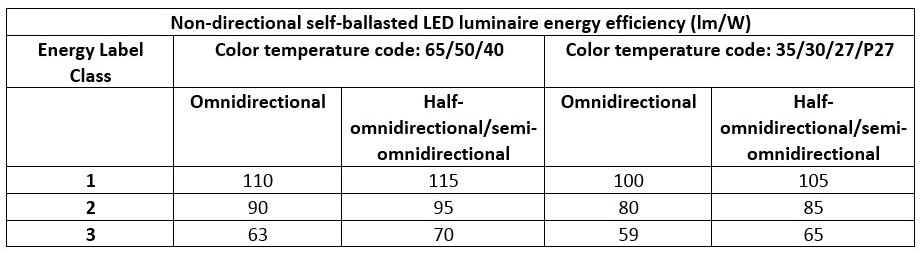
|
|
Chinese Energy Efficiency Labels for non-directional self-ballasted LED lights. |
1.2 Non directional self-ballasted LED light performance demands
Non directional self-ballasted LED light performances must meet GB/T24908 standard. The standard GB/T24908-2014 describes non directional self-ballasted LED light efficiency performance, power factor, luminous flux, color temperature, lifetime, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). The standards are also classified into three classes, as seen in table two below.
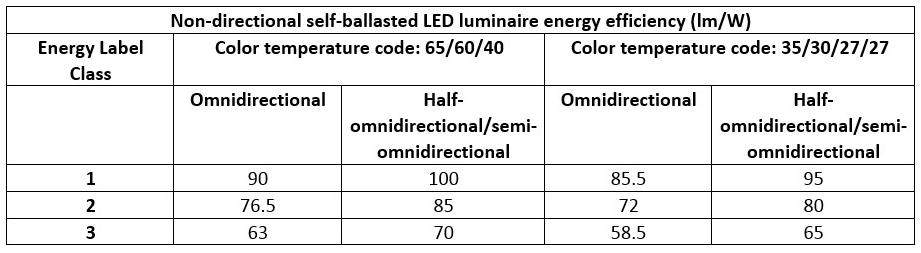
|
|
Chinese Energy Efficiency Labels for non-directional self-ballasted LED lights. |
It can be seen from table 1 and table 2, GB30255-2013 self-ballasted LED light efficiency standards is much higher than GB/T24908-2014. Manufacturers need to consider both standards when manufacturing products to ensure it meets the regulations outlined in GB30255-2013.
2. The EU directive on energy-related products (ErP)
ErP standards listed energy consumption products for average and special lighting environments, and the standards are mostly designed to meet these standards.
2.1 LED light efficiency levels
EU No. 874/2012 energy label standards target incandescent bulbs, fluorescent lights, HID lamps, LED lamps and module usage. Different energy labels are applied to the above listed lighting types sold on the market, which have set clear standards. The regulation separates lights into two major categories directional lighting and non-directional lighting, and offers Energy Efficiency Index (EEI) regulations as seen in table three.

|
EEI calculations and related equations:
EEI=Pcor/Pref
Pcor: Pcor is the rated power measured at nominal input voltage and corrected where appropriate in accordance with Prated. In LED lights the addition of an external control device is calculated by multiplying the Prated with a coefficient of 1.1. In other situations, the Pcor is equivalent to thePratedvalue.
Pref: is the reference power obtained from the useful luminous flux of the lamp (Φuse) using the following formula:
For models with Φuse < 1,300 lumen:

|
(equation 2)
For models with Φuse ≥ 1,300 lumen: Pref = 0.07341Φuse (equation 3)
Φuse is defined as follows:
— directional lamps with a beam angle ≥ 90° other than filament lamps and carrying a warning on their
packaging in accordance with point3.1.2(j) of this Annex: rated luminous flux in a 120° cone (Φ120°)
— other directional lamps: rated luminous flux in a 90° cone (Φ90°).
2.2 Non directional residential LED light standards
EC No 244/2009 regulations have split LED lights into transparent and opaque lights, with Pmaxrepresenting the maximum rated power. The maximum rated power is closely related to luminous flux(Φ). Further details can be seen in table four.

|
2.3 Directional LED light energy efficiency standards
EU No 1194/2012 regulation split LED lights into two major classes, directional LED lighting and non-directional lighting. However, this particular regulation only addresses directional LED lighting energy efficiency. The directive implemented in Sept. 1, 2015 requests directional LED lights maximum energy efficiency index (EEI) cannot exceed 0.50, and by 2016 LED lights cannot exceed 0.20. Additional requirements include the light’s survival factor and lumen maintenance must meet 6,000 hours, its starting time has to be less than 0.5 seconds, while the lamp warm-up time has to reach luminous flux 95% in less than 2 seconds. Other performance standards also include premature failure rate, color rendering (Ra), color consistency, lamp power factor (PF) for lamps integrated with gear. In total the standard covers nine major indicators for LED lights .
The EU lighting energy efficiency standards and directives indicate the ErP is only regulating non directional LED light energy efficiency for the time being. Directional LED light standards have to meet EC No244/2009 standards, while LED energy efficiency labels and classification are determined by EU No 874/2012 standards.
3. U.S.ENERGY STAR label
ENERGY STAR is a joint electronic energy efficiency certification project launched by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the Environmental Protection Agency. The project has listed specific regulations for LED engines and lights used in residential applications, products that meet its energy standards can receive the ENERGY STAR label.
3.1. LED light engine energy efficiency requirements
ENERGY STAR® Program Requirements for Residential Light Fixtures Eligibility Criteria – Version 4.2 mostly covers residential lighting or outdoor lighting energy efficiency standards. Uncovered LED light engines energy efficiency must be greater than 50 lm/W, while covered LED engines light efficiency has to be greater than 40 lm/W.
3.2 Energy efficiency requirements for integral LED lamps
ENERGY STAR® Program Requirements for Integral LED Lamps-version 1.4 regulates integral LED lighting luminous efficacy, lumen output, luminous intensity distribution, color temperature, LED operating frequency, operating voltage, CRI, audible noise, packaging and others. None standard LED lights with power below 10W, and non directional LED lighting luminous efficacy has to be greater than 50 lm/W. Luminous efficacy standards for none standard LED lights with a power greater than 10W and none directional LED lights need to be greater than 55 lm/W. Decorative LED lighting luminous efficacy needs to be higher than 40 lm/W, while directional LED lighting luminous efficacy varies according to the lighting size. Lights with a diameter ≤20/8-inch needs to be greater than 45 lm/W.
Conclusion
A comparison of lighting energy efficiency standards between the EU,U.S.andChinaindicatesChina’s LED lighting standards are very similar to ENERGY STAR. Both countries energy efficiency standards are based on luminous efficiency, but the U.S. ENERGy STAR LED light energy efficiency standards and regulations cover a much wider scope, and research and updates occur much faster. However,China’s minimum energy efficiency standard for non-directional LED light is about 20% higher than ENERGY STAR.
The EU LED light energy standard is very different from Chinese or U.S. ENERGY STAR as it is determined by EEI. From the formula listed in 2.1, it can be said a LED light’s EEI calculation is based on power factor, total luminous flux, beam angle, and useful luminous flux. Apparently, the whole process is much more complicated and would raise company’s test costs.
Since Chinese LED light energy efficiency standards are short of sufficient research and development process, the country should make more cooperations with EU orU.S.and other countries.Chinashould also use EU andU.S.energy efficiency standards as a reference to formulate lighting efficiency standards. Besides, under Chinese government guidance, major or leading Chinese LED companies especially should focus on product quality, volume, and safety standards. Companies are encouraged to improve their product quality and actively participate in forming new standards, especially new products. The final purpose is for companies to innovate, and research new standards to aid the country transition from “Manufactured inChina” to “Created inChina.”


